Every network-compatible device can be identified by its MAC (media access control) address, a unique 17-character string of letters, numbers and colons. GeForce NOW transforms underpowered or incompatible hardware into high-performance GeForce gaming rigs. Now, we’re bringing the world of PC gaming to iOS devices through Safari. GeForce NOW is streaming on iOS Safari, in beta, starting today. That means more than 5 million GeForce NOW members can now access the latest experience by launching Safari from Read article.
- Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future Reference In Excel
- Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future Reference Free
- Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future References
- Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future Reference Online
- Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future Reference Chart
| Ethernet |
Description:
| Protocol suite: | Ethernet |
| Type: | CSMA/CD Data Link and Physical Layer. |
The Ethernet is a local area network (LAN) set of protocols which serves the physical and data link layers. Ethernet utilizes a linear bus or star topology. Ethernet served as the basis for the IEEE 802.3 standard.
The Ethernet deals with the low level - Physical and Data Link Layers.
The Data Link Layer is divided into two sublayers:
- Logical Link Control (LLC). This sublayer establishes the transmission paths between computers or devices on a network.
- Media Access Control (MAC). On a network, the network interface card (NIC) has an unique hardware address which identifies a computer or peripheral device. The hardware address is used for the MAC sublayer addressing. Ethernet uses the MAC hardware addresses for the source and destination for each packet transmitted.
Ethernet uses CSMA/CD when transmitting packets. The Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is an algorithm, for transmitting and receiving packets over a common network hardware medium, by aiding in avoiding transmission collisions. The network is checked for other transmissions; when the way is clear, the computer transmissions can begin. If a collision is detected the packet is retransmitted later.
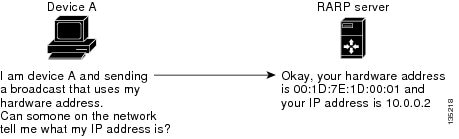
Address resolution protocol (ARP) is a TCP/IP protocol used to map IP network addresses to a hardware interface physical addresses.
Reverse address resolution protocol (RARP) is a TCP/IP protocol used to map hardware interface physical addresses to IP network addresses.
Some of the listed RFCs for Ethernet implement the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
Ethernet frame.
| Preamble | Ethernet 802.3 packet | Data | FCS |
Preamble. 8 bytes.
For synchronization, this indicates that the frame is about to begin. Included is the Start Frame Delimiter field that ends with two1s.
Ethernet 802.3 Packet format.
| 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Destination Address | |||||||||||||||
Source Address | |||||||||||||||
| EtherType | |||||||||||||||
| Data ::: | |||||||||||||||
Destination Address. 6 bytes.
The address(es) are specified for a unicast, multicast (subgroup), or broadcast (an entire group).
Source Address. 6 bytes.
The address is for a unicast (single computer or device).
EtherType. 16 bits.
Which upper layer protocol will utilized the Ethernet frame.
Data. variable, 46-1500 bytes.
FCS, Frame Check Sequence. 4 bytes.
Error checking with a Cycle Redundancy Check (CRC) value.
Ethernet 802.2 LLC Packet format:
| 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSAP | |||||||
| SSAP | |||||||
| Control | |||||||
LLC, Link Layer Control.
The Logical Link Control (LLC) consists of the DSAP, SSAP, and Control fields. The function is to establish paths to the SAP addresses for the Network Layer protocol services. This part gets inserted into the data field.
DSAP, Destination Service Access Point. 8 bits.
The destination network layer, protocol type of the packet.
SSAP, Source Service Access Point. 8 bits.
The source network layer, protocol type of the packet.
Control. 8 bits.
Ethernet SNAP Packet format:
| 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organization Code | |||||||
| EtherType | |||||||
Ethernet SNAP. Organization Code and Ethertype fields follow the LLC fields.
Organization Code. 3 bytes.
Which organization assigned the Ethernet Type field.
EtherType. 2 bytes.
Defines which upper layer protocol will utilize the Ethernet frame.
| Value | EtherTypes |
|---|---|
| 0x0800 | IP. |
| 0x0806 | ARP, Address Resolution Protocol. |
| 0x8035 | RARP, Reverse Address Resolution Protocol. |
| 0x809B | AppleTalk. |
| 0x80F3 | AppleTalk ARP. |
| 0x8137 | NetWare IPX/SPX. |
Glossary:
Address Mapping.
(RFC 894, page 2) Mappings between 32-bit Internet addresses and 48-bit Ethernet addresses could be accomplished through the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) [RFC 826]. Internet addresses are assigned arbitrarily on some Internet network. Each host's implementation must know its own Internet address and respond to Ethernet Address Resolution packets appropriately. It should also use ARP to translate Internet addresses to Ethernet addresses when needed.
Managed Objects.
(RFC 2358, page 3) Managed objects are accessed via a virtual information store, termed the Management Information Base or MIB. Objects in the MIB are defined using the subset of Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1) [Information processing systems - Open Systems Interconnection - Specification of Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1), International Organization for Standardization, International Standard 8824, December 1987.] defined in the SMI [RFC 1902]. In particular, each object object type is named by an OBJECT IDENTIFIER, an administratively assigned name. The object type together with an object instance serves to uniquely identify a specific instantiation of the object. For human convenience, we often use a textual string, termed the descriptor, to refer to the object type.
SNMP, Network Management Framework.
(RFC 2358 , pages 2 and 3) The SNMP Network Management Framework consists of several components. For the purpose of this specification, the applicable components of the Framework are the SMI and related documents [RFC 1902, RFC 1903, RFC 1904], which define the mechanisms used for describing and naming objects for the purpose of management. The Framework permits new objects to be defined for the purpose of experimentation and evaluation.
RFCs:
Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future Reference In Excel
[RFC 826]An Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol.
[RFC 894] A Standard for the Transmission of IP Datagrams over Ethernet Networks.
[RFC 895] A Standard for the Transmission of IP Datagrams over Experimental Ethernet Networks.
[RFC 1029] A MORE FAULT TOLERANT APPROACH TO ADDRESS RESOLUTION FOR A MULTI-LAN SYSTEM OF ETHERNETS.
[RFC 1089] Nada dering line mp3. SNMP over Ethernet.
[RFC 1369] Implementation Notes and Experience for The Internet Ethernet MIB.
[RFC 1643] Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-like Interface Types.

- Obsoletes: RFC 1284, RFC 1398, RFC 1623.
[RFC 1972] A Method for the Transmission of IPv6 Packets over Ethernet Networks.
[RFC 2358] Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-like Interface Types.
- Obsoletes: RFC 1650.
Obsolete RFCs:
[RFC 1284] Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-like Interface Types.
[RFC 1398] Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-like Interface Types.
[RFC 1623] Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-like Interface Types.
[RFC 1650] Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-like Interface Types using SMIv2.
References:
Chappell, Laura and Dan Hakes. Novell's Guide to NetWare LAN Analysis (First Edition). Sybex Inc. and Novell Press, 1993.
Chappell, Laura and Dan Hakes. Novell's Guide to NetWare LAN Analysis (Second Edition). Sybex Inc. and Novell Press, 1994.
Naugle, Matthew. Network Protocol Handbook. McGraw-Hill, Inc., 1994.
Networking Technologies. Novell Inc.
Latest News: Check out what’s new for business this fall. Learn more about what's new for business
When the world changes, business changes too. Apple hardware, software, and services work together to give your employees the power and flexibility to do whatever needs doing — wherever that may be.
With great power comes great productivity.
Apple hardware, software, and services work together to deliver a seamless experience that just works. You can start a project on Mac and finish it on iPad, use your screens side by side to extend your workspace, and even draw with Apple Pencil on your iPad or use your iPhone to make live updates on your Mac. And it’s all compatible with apps from Microsoft and Google, so your team has everything it needs to get any job done.
Mac
Bring your biggest projects to life. Every Mac is designed for powerful performance — so you can build complex spreadsheets, create stunning presentations, or multitask across multiple projects.
iPad
Get power that outpaces most PC laptops in a design that goes everywhere. Scan merchandise, visualize models in 3D, and breeze through work when you multitask with Split View.

iPhone
Do incredible things on the go. Visualize 3D projects using augmented reality. Collaborate with your team on Keynote presentations. And stay connected with FaceTime, Messages, and Mail.
Apple Watch
Stay connected at a glance. Handle notifications as they pop up with a single tap, track Messages, and get the most out of apps for work and wellness.
Apple TV
Turn your best work into a cinematic experience. Put important presentations and>
Success Story - Capital One
Capital One
When people love what they do, what they do is amazing.
Anything’s possible with apps.
Apple devices come with powerful apps built in. The App Store offers even more tools for almost any job — from sales and engineering to fixing jets and building skyscrapers. And the Apple developer platform gives businesses the power to create custom solutions that the world has yet to see.
Built-in Apps
Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future Reference Free
Notes, Siri Shortcuts, and Reminders make simple things even easier, like signing and scanning documents to share and adding a sketch with Apple Pencil on iPad.
App Store
Over 235,000 business apps help you get any job done, like Cisco Webex and Microsoft Excel for daily needs and industry-specific tools like Shapr3D and Scandit for specialized tasks.
Custom Apps
Build your own game-changing apps using cutting-edge technology for whatever your business needs.
Success Story - BSH
BSH
Custom apps make employees, and customers, happier.
Zero-touch
deployment is a
snap for IT.
Apple Business Manager makes Apple devices exceptionally easy to deploy and manage. IT can push apps and create Managed Apple IDs, and employees can customize their devices on their own.
Security first, second, and third.
Apple devices and platforms are designed to keep your personal data and corporate information secure. Key security features, like hardware-based device encryption, can’t be disabled by mistake. Touch ID and Face ID make it easy to secure every device. And because many of these features are enabled by default, employees and IT won’t need to perform extensive configurations.
Success Story - BDC
BDC
iPad made it possible to close small business loans onsite.
Apple Business
Manager
Deploy devices and apps and create Managed Apple IDs for every employee in one place.
AppleCare for
Enterprise
Support your IT team, repair or replace hardware, and train employees to get the most out of every Apple product.
Apple Financial
Services
Find flexible terms and end‑of‑lease options to get the most value from your investment.
Apple Professional Services
Get all your Apple devices up and running with hands‑on help from Apple engineers.
Apple Training
Prepare your IT team and in‑house developers to deploy Apple products and build custom apps.
Privacy
Every Apple product is built from the ground up to protect your privacy. We don’t create user profiles, sell personal information, or share data with third parties to use for marketing or advertising. And apps share only the information that you authorize.
Environment
Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future References
Apple products are designed to reduce our impact on the planet while maximizing performance and strength. We strictly monitor our supply chain during manufacturing, are careful to design for energy efficiency, and work to make our products as recyclable as possible.
Accessibility
We build Apple products to empower everyone. Every device, every piece of software, and every service is created with accessibility features built in. Because when everyone can participate in the ways that work best for them, people and businesses are at their best.
How to Buy
We’re here to help you find the best, most cost‑effective solution for your business, whether you’re a one-person team or 10,000 strong.
Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future Reference Online
Apple at Work
in action.
See how businesses are using Apple products to create extraordinary experiences for their employees and their customers.
Where Are Mac Addresses Stored For Future Reference Chart
Reports and Resources
Products and Platform
Apps
IT
